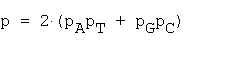Assessing the significance of repeats Let's calclulate the mean repeats number (l,k) in a random sequence consisting of N nucleotides occurring with frequencies p1,p2,...,pm, where m=4 - is the number of various nucleotide types. The probability of two nucleotides being identical is: The probability of two random sequence segments of length l differ by k nucleotides is
where p is from (1), C l - is the permutation number of k differences in l positionsThe number of possible mutual locations of two non-overlapping segments of length l nucleotides could be calculated as follows. The first segment could be located in N-2*l+1 positions of the sequence. If the frist segment starts from i-th position, then the second one could be located in N-i-2*l+2 positions with non-overlapping. Thus the overall number of nonoverlapping pairs of segments is
Mean number of repeats in a random sequence of length N is calculated as:
Let's consider only repeats (l,k) which occur for 1 time in a sequence of length N on the average. In this case we can use the binomial distribution to assess the probability of finding exactly n repeats (l,k) in a target sequence. This probability equals:
Then we find threshhold no given a significance level q that satisfies: If the repeat number exceeds the threshold n(l,k) > no(l,k), then we consider the number n as significantly deviating from the mean number En(l,k) for a significance level q= 0.05, and the repeat found in n copies we call the nonrandom one. The formulae considered are valid for the direct, complementary, symmetrical and inverse repeats. In case of complementary repeats and inverse ones we use the probability of nucleotides to complement each other instead of (1), that is:
References for statistical basis
Program description The program is destined to search for non-perfect repeats of various types in a nucleotide sequences.
Definitions 1. Non perfect repeat is a pair of DNA segments of length l differing one from another by k nucleotides. This pair of segments is called (l,k) repeat. 2. The overall set of (l,k) repeats is called (l,k) group.
Depending on type of correspondence we consider the following types of repeats: Direct repeat - two (l,k) segments are located in the same orientation in a single DNA strand; Symmetrical - two (l,k) segments are located in opposite orienation in a single DNA strand;. Direct complementary repeats - two segments are located in the same orientation in different DNA strands;. Inverse repeats - two segments are located in oppsite orientation in the different DNA strings.. Program features The program performs the repeats search by group clusters (l,k). After the search the optimization procedure follows consisting of the following steps:
Program Parameters Repeats types to search parameters
Direct Repeats - turns on the search of direct repeats ;
Direct Complementary Repeats - turns on the search of direct complementary repeats;
Symmetric Repeats - turns on the search of symmetric repeats;
Invert Repeats - turns on the search of invert repeats.
Parameters specifying the features of group (l,k) to search min length (l1), max length (ln), Limit type, Limit are the parameters to define the set of groups (l,k) that are subject to search:
Number of mismatches ki depends on statistical threshold given by no(l,k) which is described above. The maximal number of mismatches is limited by max mismatch number parameter.
min length - the minimal length of the repeated segment max length -the maximal length of the repeated segment max mismatch number -the maximal mismatch number
Limit type - Statistical threshold type. Can be of two values:
Selection of statistically significant (l,k) groups Save Mode - Statistical significance switch. - if Save Mode= NOT RANDOM, accepted are groups (l,k), having nonrandom number of repeats; - if Save Mode= ALL, accepted are all groups (l,k) |
|
|
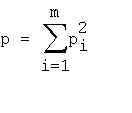 (1)
(1)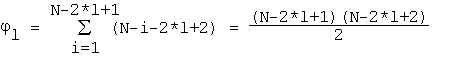
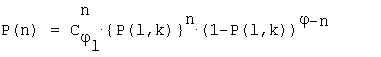
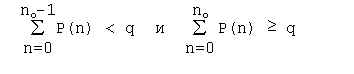 (4)
(4)